Your Guide to Low Power Wireless Communication
Low power wireless communication is a game-changer for industries that need efficient, long-lasting, and reliable connectivity.
Think about it: lower energy use means longer battery life and fewer headaches. This is a big deal for IoT, industrial automation, and healthcare, where staying connected is non-negotiable.
Take IoT and smart devices, for example. Low power wireless sensors keep the data flowing without needing constant battery swaps. This keeps your smart systems humming along smoothly.
In healthcare, wearable devices with low power tech can monitor patients around the clock, making sure doctors can step in right when they’re needed.
In this guide, we look at why low power wireless matters and how you can use it to leverage your electronic product development.

Perks of Low Power Wireless Communication
Switching to low power wireless communication can seriously boost performance and cut down on costs.
Here’s why:
- Energy Efficiency: These technologies sip power, making them perfect for battery-operated devices. This means your gadgets run longer before needing a recharge or new batteries.
- Cost Savings: Using less energy means lower bills. Plus, devices last longer and need less maintenance, saving you even more money.
- Scalability: Got a growing number of devices? No problem. Low power wireless networks can easily expand, making them ideal for big projects like smart cities and industrial setups.
- Reliability: Designed to be tough, these protocols ensure your data gets through, even in tricky environments. This is crucial for applications where failure isn’t an option.
- Flexibility: With options like Bluetooth Low Energy, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN, you can pick the tech that fits your needs best.
Technology | Power Use | Range | Data Speed | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) | Very Low | 100 metres | 1 Mbps | Low |
Zigbee | Low | Up to 200 metres | 250 kbps | Medium |
LoRaWAN | Low | 15-20 kilometres | 50 kbps | High |
Want to dive deeper? Check out our article on low power wireless technologies and low power wireless protocols.
Grasping the importance and perks of low power wireless communication helps you make smart choices for your organisation.
By picking the right tech, you can boost efficiency, cut costs, and keep everything connected smoothly.
Uses of Low Power Wireless Tech
Let’s look at the ways low power wireless tech is making life easier and more efficient. From smart homes to industrial automation and healthcare gadgets, this tech is everywhere.
Smart Homes and Gadgets
Low power wireless tech is a game-changer for the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart gadgets. These devices often run on batteries and need to be energy-efficient to last longer.
Device / System | Power Use (mW) | Data Speed (Kbps) | Range (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
Smart Lights | 10 – 30 | 250 | 100 |
Smart Thermostats | 20 – 50 | 250 | 100 |
Home Security | 15 – 40 | 250 | 150 |
Industrial Automation
In factories and industrial settings, low power wireless tech helps with monitoring and control systems. These systems need to be reliable and quick to keep things running smoothly and save energy.
System | Power Use (mW) | Data Speed (Kbps) | Range (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
Remote Monitoring | 30 – 70 | 250 | 100 |
Predictive Maintenanace | 20 – 60 | 250 | 150 |
Asset Tracking | 10 – 40 | 250 | 300 |
Health and Wearables
Low power wireless is a staple technology in healthcare and wearables. These devices need to be light, portable, and able to run for a long time without needing a charge.
Device | Power Use (mW) | Data Speed (Kbps) | Range (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
Fitness Trackers | 5 – 20 | 125 | 10 |
Medical Implants | 1 – 5 | 50 | 2 |
Remote Patient Monitoring | 10 – 30 | 250 | 100 |
Low power wireless tech is essential in these areas, providing the efficiency, reliability, and range needed for top performance.
Key Tips for Low Power Wireless Solutions
When you’re working with low power wireless communication, there are a few things to bear in mind to make sure everything runs smoothly.
We’re talking about range and coverage, power consumption, and data rate and latency.
Here are some factors to consider for your product development…
Range and Coverage
Low power wireless is a staple technology in healthcare and wearables. These devices need to be light, portable, and able to run for a long time without needing a charge.
Application | Required Range (m) |
|---|---|
Smart Home Devices | 10 – 20 |
Industrial Automation | 50 – 200 |
Healthcare Wearables | 1 – 10 |
Picking the right protocol is key. For example, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) works great for short distances, while LoRaWAN is your go-to for longer ranges.
Power Consumption
If your device runs on batteries, power consumption is a big deal.
Lower power use means longer battery life, which means less hassle with replacements and maintenance. Different wireless technologies use varying amounts of power.
Protocol | Average Power Use (mW) |
|---|---|
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) | 10 – 100 (dependent upon how much data is being transferred and how often it’s being sent/received) |
Zigbee | 10 – 100 |
LoRaWAN | 0.5 – 10 |
Data Rate and Latency
How fast can your system send data, and how quickly does it respond?
Data rate is the speed of data transfer, while latency is the delay between sending and receiving data.
Various uses can accomodate different speeds and delays.
Application | Required Data Rate (kbps) | Acceptable Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
Smart Home Devices | 10 – 250 | 50 – 200 |
Industrial Automation | 250 – 1000 | 20 – 100 |
Healthcare Wearables | 10 – 100 | 100 – 500 |
Balancing data rate and latency is key to meeting your needs. For example, industrial automation needs higher data rates and lower latency compared to smart home devices.
By keeping these tips in mind, you’ll be better equipped to make smart choices for your low power wireless projects.
Think about range and coverage, power use, and data rate and latency to ensure everything works perfectly.
For more insights, explore the various low power wireless technologies available.
Discover more about low power wireless communication standards and protocols - download your copy now

Types of Low Power Wireless Protocols
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is your go-to for short-range comms between devices without draining the battery.
Perfect for gadgets that need to talk now and then, BLE keeps the power usage low while still offering data speeds up to 2 Mbps. It hangs out in the 2.4 GHz band.
Parameter | BLE |
|---|---|
Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz |
Data Rate | Up to 2 Mbps |
Range | Up to 100 metres |
Power Consumption | Low |
You’ll find BLE in things such as low power wireless sensors and wearables because it’s super efficient and reliable.
Want more on BLE? Read this guide on low power wireless protocols.
Zigbee
Zigbee is the champ for creating mesh networks with low power. It’s a favourite for setups needing dependable, scalable communication at lower data rates.
Zigbee works in the 2.4 GHz, 915 MHz, and 868 MHz bands, pushing data up to 250 kbps.
Parameter | Zigbee |
|---|---|
Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz, 915 MHz, 868 MHz |
Data Rate | Up to 250 kbps |
Range | 10-100 metres (extendable with mesh network) |
Power Consumption | Low |
Zigbee shines in low power wireless networks for smart homes and industrial automation. Its mesh network boosts coverage and reliability.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is the long-distance runner in the low power game. It’s built for sending small data packets over huge distances, making it perfect for smart cities and farm tech.
LoRaWAN operates in sub-GHz bands like 433 MHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz, with data rates from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps.
Parameter | LoRaWAN |
|---|---|
Frequency Band | 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz |
Data Rate | 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps |
Range | Up to 15 km in rural areas, 2-5 km in urban areas |
Power Consumption | Very Low |
LoRaWAN’s range and power efficiency make it a hit in low power wireless technologies, especially for remote monitoring and IoT.
Knowing these protocols helps you pick the right low power wireless solution for your needs.

Real-Life Wins with Low Power Wireless Communication
Here are some success stories where low power wireless communication has made a real difference. Discover how it’s shaking things up in manufacturing, smart homes, and healthcare.
Manufacturing Magic
In factories, low power wireless communication is like having a superpower.
By using low power wireless sensors, companies can keep an eye on their systems and processes in real-time.
This means fewer breakdowns and more efficient operations.
Application | Required Data Rate (kbps) | Acceptable Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
Smart Home Devices | 10 – 250 | 50 – 200 |
Industrial Automation | 250 – 1000 | 20 – 100 |
Healthcare Wearables | 10 – 100 | 100 – 500 |
Smart Home Wonders
Smart homes are getting a major boost from low power wireless communication. Think smart thermostats, lights, and security cameras that use low power wireless tech to make your home more convenient and energy-efficient.
Application | Required Data Rate (kbps) | Acceptable Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
Smart Home Devices | 10 – 250 | 50 – 200 |
Industrial Automation | 250 – 1000 | 20 – 100 |
Healthcare Wearables | 10 – 100 | 100 – 500 |
Healthcare Heroes
In healthcare, low power wireless communication is a game-changer. It’s behind those nifty wearable devices and remote monitoring systems that keep tabs on patients without being a pain.
Application | Required Data Rate (kbps) | Acceptable Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
Smart Home Devices | 10 – 250 | 50 – 200 |
Industrial Automation | 250 – 1000 | 20 – 100 |
Healthcare Wearables | 10 – 100 | 100 – 500 |
Low power wireless communication is making a big splash in these and many other sectors. By using low power wireless networks and protocols, businesses can work smarter, save money, and give end users a better experience.
Low Power Wireless Design Projects and Case Studies
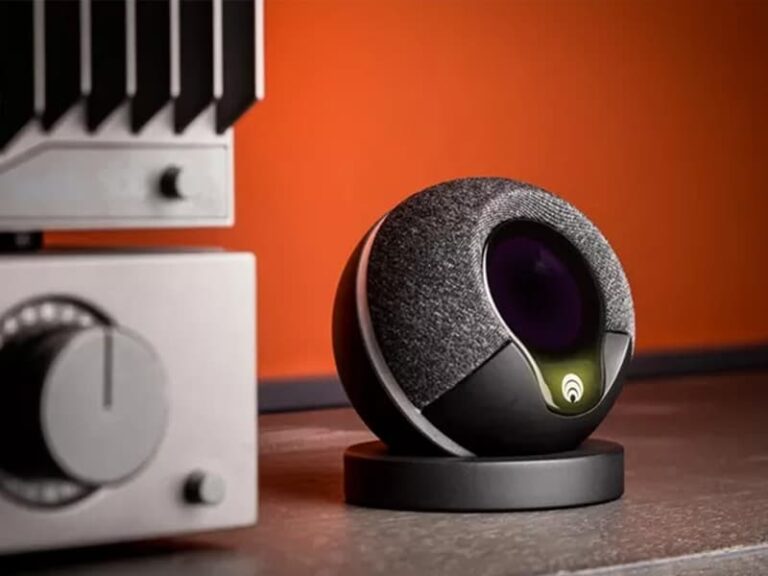

Award-winning smart home security system
Discover how ByteSnap overcame complexities with pcb constraints, thermal issues and wireless performance requirements to help develop this smart home security system...
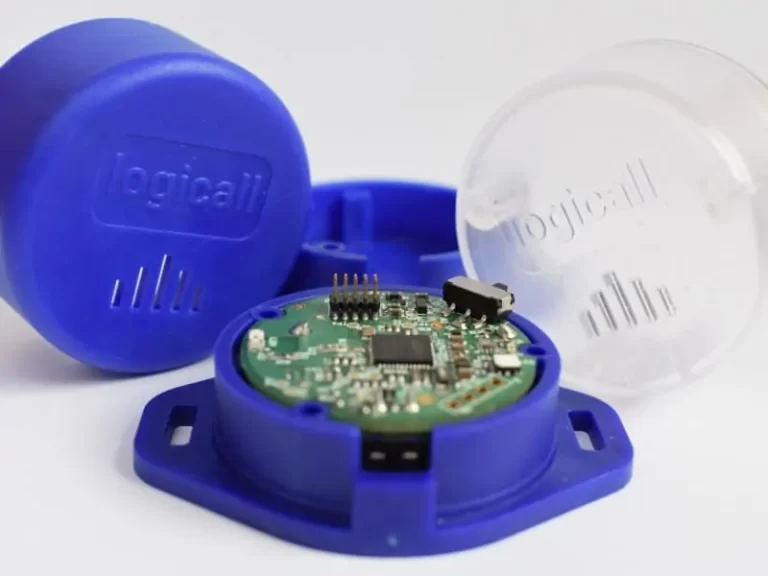

Lab Monitoring Headache Cured with Low Cost Bluetooth Solution
Read how we developed a low-cost Bluetooth solution for laboratory monitoring devices that measure temperature, humidity, and other variables, while ensuring data collection and alerts via an Android app.

World First's 8-channel Ultrasonic IoT Device
Ultra-low power: we helped to design the world's first 8-channel ultrasonic IoT device that operates in Zone 0 environments, with 5 years+ battery life and 200m communication distance using Bluetooth 5.0.
Picking the Right Electronic Product Development Partner
Choosing the right design partner can make or break your low power wireless project.
You want someone with a proven track record and a deep understanding of low power wireless technologies.
Look for these qualities:
- Experience and Know-How: They should have plenty of experience in low power wireless communication.
- Tech Skills: They need to be good with various low power wireless protocols like BLE, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN.
- Innovation: They should be able to come up with creative solutions that fit your needs.
Teaming Up for Custom Solutions
You need custom solutions that fit your specific needs. Working closely with your development partner can help you create low power wireless systems that match your goals.
Here’s what to focus on:
- Requirement Analysis: Make sure you and your partner understand exactly what you need.
- Prototyping and Testing: Work together on prototypes and test them to get things just right.
- Integration: Ensure everything works smoothly with your existing low power wireless networks.
Staying on the Right Side of Regulations
On regulatory compliance, your partner should know the ins and outs of the relevant rules and standards.
Key focus areas:
- Local and International Standards: Make sure you comply with standards like CE and FCC.
- Certification Processes: Know what certifications you need and how to get them.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records to make regulatory approvals easier.
Regulatory Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Local Standards | Follow local regulatory rules |
International Standards | Stick to global standards like FCC |
Certification | Get the necessary certifications |
Documentation | Keep thorough documentation |
By paying attention to these areas, you can build a strong partnership that delivers efficient and compliant low power wireless solutions.
Need extra engineering resource for your low power product design?
Knowledge Panel
What are the advantages of using low-power wireless communication?
Low-power wireless communication offers advantages like extended battery life, reduced power consumption, cost-effectiveness, and improved reliability. These systems are ideal for IoT devices, wearable technology, and smart home applications where power efficiency is crucial for long-term performance.
What are the common protocols used in low-power wireless communication?
Common protocols used in low-power wireless communication include Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee, Z-Wave, LoRa (Long Range), and NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT). Each protocol has its unique characteristics and applications, catering to different needs in the low-power wireless communication landscape. For instance, some are short range, others for long distances. Discover more in our IoT Standards and Protocols Guide.
Which wireless technology has the lowest level of power consumption?
The wireless technology that has the lowest level of power consumption is Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). This technology is specifically designed for low-power applications, making it ideal for devices that need to conserve battery life while maintaining a wireless connection.
How does low-power consumption impact the range and reliability of wireless communication?
Interference and low signal strength can disrupt communication in low-power wireless systems, leading to packet loss, delays, and reduced network coverage. To combat this, techniques like frequency hopping, power control, and error correction coding are employed to improve reliability and performance.
How can advances in technology improve the efficiency of low-power wireless communication systems?
Advances like low-power consumption components, efficient protocols, and optimised wireless networks enhance low-power wireless communication systems. Integration of IoT devices with low-power communication technology and improvements in battery life performance also contribute to improved efficiency in communication systems.

With over 30 years of experience in electronics design and manufacturing, Conrad brings a wealth of knowledge to the ByteSnap team. His extensive career has spanned diverse industries, including the petrochemical, industrial, security, and commercial sectors.
Previously, Conrad’s entrepreneurial spirit led him to establish and manage his own PCB population factory in South Africa. This hands-on experience deepened his understanding of the intricacies of electronics manufacturing.
Conrad’s decision to join ByteSnap was driven by his desire for continuous growth and the opportunity to work with a UK-leading electronics design house. He says, “Working at ByteSnap is interesting, challenging, and completely enjoyable.”
Away from circuits and components, Conrad enjoys exploring new places, museums, and football.